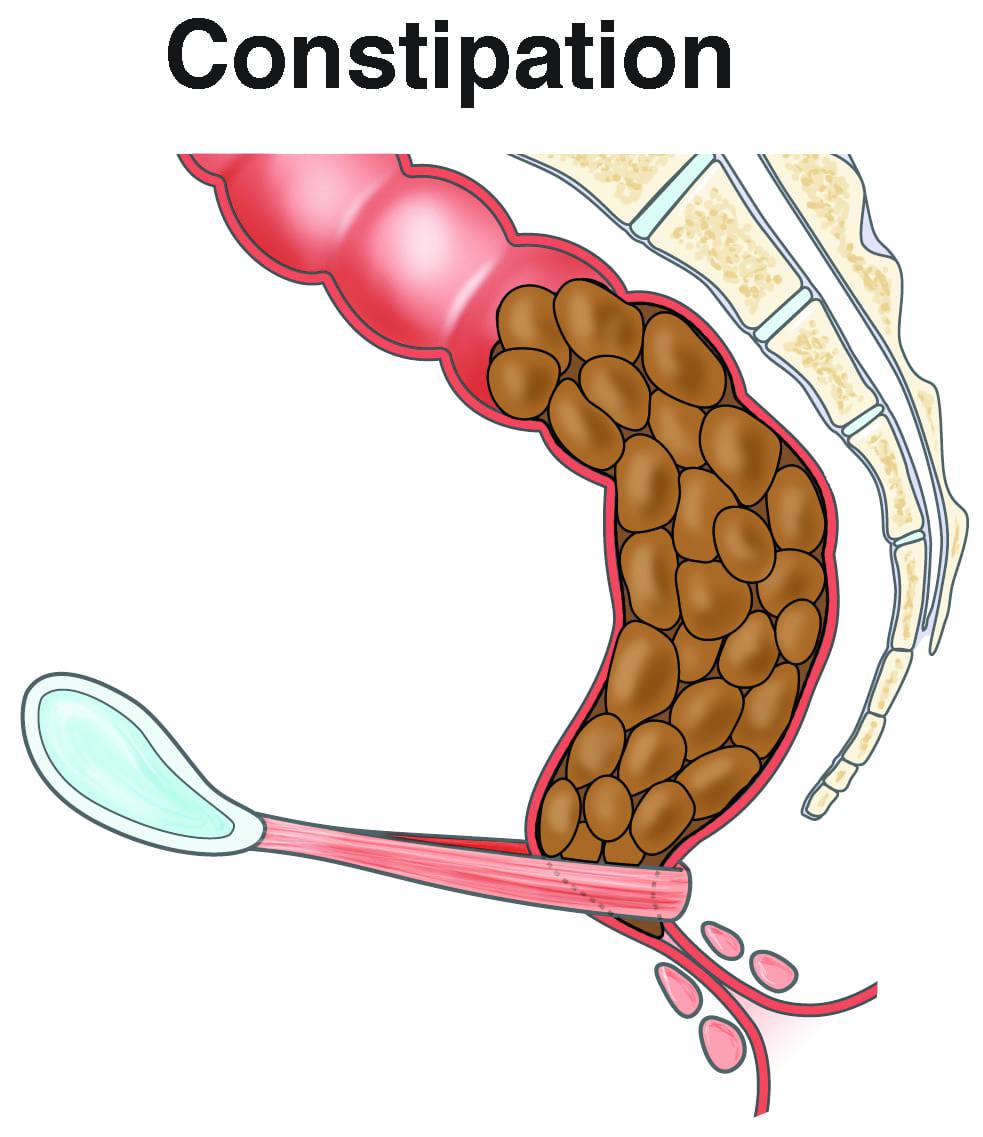
Constipation is a common digestive issue that affects people of all ages. It occurs when bowel movements become infrequent or difficult, leading to discomfort and frustration. Several factors contribute to constipation, making it essential to understand its causes and adopt preventive measures.
Causes of Constipation:
- Inadequate Fiber Intake: Diets low in fiber can slow down the digestive process, resulting in hard and dry stools that are difficult to pass.
- Lack of Physical Activity: A sedentary lifestyle can lead to sluggish bowel movements as exercise helps stimulate the digestive system.
- Dehydration: Insufficient water intake can cause stools to harden and make them challenging to pass.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as opioids and antacids, can cause constipation as a side effect.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during pregnancy, can contribute to constipation.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and hypothyroidism may lead to chronic constipation.
Preventive Measures:
- Increase Fiber Intake: Include more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your diet to promote regular bowel movements.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to keep stools soft and easier to pass.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activity regularly to stimulate the digestive system and maintain healthy bowel movements.
- Establish a Toilet Routine: Try to go to the bathroom at the same time each day to regulate bowel movements.
- Limit Medication Use: If possible, avoid medications that are known to cause constipation or discuss alternatives with your healthcare provider.
- Address Underlying Conditions: If you suspect an underlying medical condition is causing your constipation, seek medical advice for proper evaluation and treatment.
By understanding the causes of constipation and implementing preventive measures, you can improve your digestive health and reduce the risk of constipation-related discomfort.
